WOOD PROTECTION
IMPLEMENTATIONS
One of the most important part of the activities of Fadoktor Mérnöki Iroda Ltd. in the field of wood protection is the elimination of damage caused by fungi, especially the dry-rot fungus and active wood-damaging insects, which damage wooden structures, wooden panelling and furniture of buildings.
An experienced team of contractors, state-of-the-art tools, methods and wood preservatives guarantee effective fungicide and insect control, which also has a preventive effect against further damage. The elimination of wood-damaging fungi and insects requires specialised knowledge, for which we have a decade and a half of experience.
Damage caused by dry-rot fungus and its elimination.
Dry rot fungus (Serpula lacrymans) causes the most dangerous damage to wooden structures of buildings.

Dry rot fungus (Serpula lacrymans)
Its fruitbody is located on the ground, but it can also appear cantilevered.
Initially it appears as a snow-white cotton ball, then it turns yellow, after intensive growth gradually reddish-brown. The edges of the thick, soft-fleshed fruitbody always remain white. Every day a considerable amount of spores, up to 1 million, can be ejected into the air from the fruitbody, which are brown and bean-shaped under the microscope. The spores retain their fertility for 2-3 years, so the risk of spreading the fungus is high if it is placed in a suitable environment for germination.
Besides the fruitbodies, the most frequently found characteristics are gray-white, plate or cord-like – fibers of the fungus on the wood, in the surrounding area andin the area of further spread. With their help, they can easily penetrate and pass through brick, stone and even concrete cracks. They can grow up to 20 m from a given settlement node in search of another decomposable wood.
The fruitbody appears in places already infiltrated by the fungal filaments about 2-3 years after settling, so the damage is not immediately noticeable. The fruitbody does not always appear that would indicate fungal damage, however, the fungal filaments are already active.
Initially, high moisture content of around 30 % is required for fungal colonisation, but subsequently 18-20 % is sufficient, as the fungus is able to condense and retain water droplets on the wood material andin the environment during wood decomposition. This provides the water needed for further decomposition. It has an optimum temperature of around 18-20 °C and can therefore be damaging in heated buildings in winter.
It is mainly a pest of built-in pine woods, but also often occurs on deciduous trees. It is the most dangerous pest of buildings because once established and spreading it is very difficult to eliminate. If even a small piece of fungal filament or spore capable of germination remains in the building after elimination, the fungus may re-grow itself under favourable conditions.
Damage should be expected after some sort of humidity appearance or leaking. If the fungus is not settled in a very intensively ventilated area, the water produced during the decompostition of wood may be sufficient to sustain its life. It is therefore self-sustaining in regards to moisture.
Under favourable conditions, the fungus can penetrate the entire building and attack the installed structural wood elements in a few years. It damages the cellulose in the wood, causing the wood to degrade, lose stability and eventually be destroyed. In wooden buildings, structural stability can be significantly reduced. In case of wooden flooring (tile, parquet), it is often noticeable that the floor collapses when it is under weight, without any warning.
Fungal spores released from the fruitbody into the environment, into the building, can cause allergic reactions in susceptible persons, which may result in nausea, headaches or other consequences of spore allergy.
To dispose of the damage, the walls must be burnt, then chemical remedial wood protection is required, using the latest and most effective foaming process and ADOLIT M wood preservative.

Burning of walls and ceiling


Foaming equipment and foaming with ADOLIT M wood preservative
Damage and elimination of wood-damaging insects
Most of the nuisances in the wooden structures of buildings are caused by wood-damaging insects. They occur much more frequently than wood-damaging fungi. They also occur in freshly laid and older wood material and can cause damage even at low moisture levels. The most common damaging insects are:


House longhorn beetle (Hylotrupes bajulus)

Out of the coniferous wood materials, that are damaged by chewing, the beetle prefers pine wood. The damage is mostly caused by the insect larvae that chew the outer part of the wood which is rich in protein, the splint. They take an average of 4 to 5 years to develop, during which time they eat large amounts of wood. They damage from late spring to early fall. They are the most common and dangerous pests of structural timber.


The furniture beetle (Anobium punctatum)

Damage caused by furniture beetle
The built-in wood is attacked and all types of wood are in danger. The damage is greater if the wood is already pre-decomposed by the fungi. Its camouflages (2-3 mm) can penetrate the wood in total cross-section. On the wood, the most characteristic evidence of the presence of the beetle are the escape openings of adult insects with a diameter of 1-2 mm. Producers re-infect the wood after flying out, so they can reproduce very well under favorable conditions.
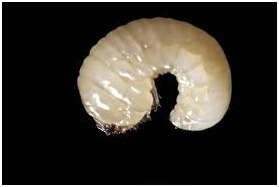

European lyctus beetle (Lyctus linearis)

Damage of European lyctus beetle
This type of beetle mainly attacks oak wood, especially parquet made of oak, tan, acacia and walnut wood. Its main nutrition is starch, which is present in the largest quantity in the sapwood layer of the wood, therefore it damages only this part of the wood. In terms of wood moisture, a value of 10-12% is optimal for its action.


Capuchin beetle (bostrichus capucinus)

Mainly the built-in oak wood is damaged by chewing of this beetle, but other hardwood species are also attacked. Its circular threads with a diameter of about 5 mm are clogged with nibbles. It attacks only the sapwood layer of the wood and does not penetrate the heartwood zone. The 7-15 mm large nuchal shield of the producer, developing from the pectoral larva, is black and the wing covers are red.
Elimination of wood-damaging insects is only possible with wood preservatives and methods developed specifically for this purpose. The execution team of our company removes insects from the wood of buildings with the use of REMMERS wood preservative, by smearing and drilling block injection.
WOOD PROTECTION IMPLEMENTATIONS REFERENCES
ABOUT US
Since 2000, Fadoktor Mérnöki Iroda Kft. and its legal predecessor have been a family business dealing with wood protection, manufacture, distribution and trade of sawmill and further processing industrial products, and especially with the design and construction of playgrounds.
CONTACT
9400 Sopron, New incubator house
Next to the Sopron-Kelet intersection of the M85 expressway. Click here for route planning!
Mo – Fr: 09:00-17:00
Dr. László Németh, CEO
Bence György Katona, Leader of Wood Protection
E-mail: bence.katona@fadoktor-mi.hu
Tel.: +3630/114-8088
Dávid Major, Leader of Planning
E-mail: david.major@fadoktor-mi.hu
Tel.: +3630/114-8099
Orsolya Szemenyeiné Bőr, Assistant
E-mail: fadoktor@fadoktor-mi.hu
Tel.: +3699/386-838
Dániel Márton, Trainee of Timberindustrie
E-mail: daniel.marton@fadoktor-mi.hu
Tel.: +3699/386-838
WHAT WE OFFER
Playgrounds
Wood protection
Outdoor equipment
Dipping tanks
Vacuum-impregnation equipment
Skateparks
© FADOKTOR MÉRNÖKI IRODA KFT. 2023 | Impressum | Privacy Policy | Website: Webpole























